Conventional Steel Structures In Chennai
1. Introduction
Conventional steel structures refer to buildings and frameworks constructed using hot-rolled steel sections and traditional connection methods such as bolting, riveting, and welding. These structures have been widely used in industrial buildings, bridges, warehouses, commercial buildings, and high-rise constructions due to steel’s high strength, durability, and versatility.
2. Materials Used
The primary material used in conventional steel structures is structural steel, typically mild steel or high-strength low-alloy steel.
Common properties:
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Ductility and toughness
- Uniformity and predictability
- Ease of fabrication and erection
Common steel grades:
- Mild steel
- High-strength steel
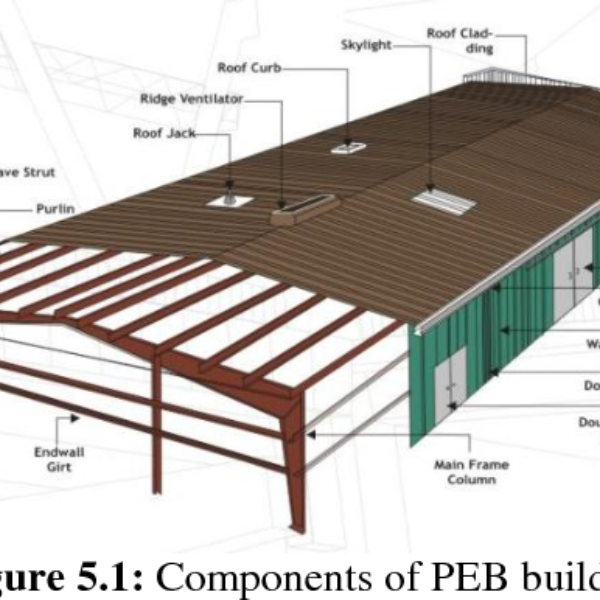
3. Structural Components
Conventional steel structures consist of standard rolled sections, including:
- Beams – I-sections, H-sections, channels
- Columns – Universal columns, box sections
- Bracing systems – Angle sections, rods
- Trusses – Angles, tubes
- Plates and gussets – Used in connections
4. Types of Conventional Steel Structures
- Rigid frame structures
- Used in industrial sheds and multistory buildings.
- Truss structures
- Common in roofs, bridges, and long-span structures.
- Portal frames
- Widely used in warehouses and factories.
- Lattice structures
- Used for transmission towers and bridges.
5. Connections in Conventional Steel Structures
Connections play a vital role in the performance of steel structures.
Types of connections:
- Bolted connections
- Riveted connections (largely obsolete but historically important)
- Welded connections
Based on behavior:
- Rigid connections
- Semi-rigid connections
- Pinned connections
6. Design Philosophy
Conventional steel structures are designed based on:
- Working Stress Method (WSM) (older practice)
- Limit State Method (LSM) (modern practice)
Design considerations include:
- Dead loads
- Live loads
- Wind loads
- Seismic loads
- Temperature effects
7. Fabrication and Erection
- Steel members are fabricated in workshops using cutting, drilling, welding, and finishing processes.
- Members are transported to the site and erected using cranes.
- Site connections are generally bolted for ease and speed.
8. Advantages
- High strength and durability
- Long span capability
- Faster construction
- Recyclability and sustainability
- Ease of modification and expansion
9. Disadvantages
- Susceptible to corrosion if not protected
- Loss of strength at high temperatures (fire)
- Requires skilled labor and quality control
- Higher initial cost compared to RCC in some cases
10. Applications
- Industrial buildings and factories
- Bridges and flyovers
- Multistory and high-rise buildings
- Warehouses and godowns
- Transmission towers and cranes
11. Maintenance and Protection
- Protective coatings (painting, galvanizing)
- Fireproofing using sprays or cladding
- Regular inspection and maintenance
12. Conclusion
Conventional steel structures remain a fundamental choice in structural engineering due to their reliability, adaptability, and proven performance. With proper design, fabrication, and maintenance, they provide economical and long-lasting solutions for a wide range of engineering applications.





