Roofing Structures In Ambattur
Roofing structures are essential components of any building, providing protection from weather elements while contributing to structural stability, aesthetics, and energy efficiency. A well-designed roofing system ensures durability, safety, and comfort for occupants.
Purpose of Roofing Structures
- Protect the building from rain, wind, heat, and snow
- Distribute loads safely to walls and foundations
- Enhance architectural appearance
- Improve thermal insulation and ventilation
Types of Roofing Structures
1. Flat Roof Structures
Flat roofs have a slight slope to allow water drainage. They are commonly used in commercial and modern residential buildings.
- Advantages: Easy maintenance, usable terrace space, cost-effective
- Materials: Reinforced concrete, waterproof membranes, bitumen
2. Pitched Roof Structures
Pitched roofs have sloping surfaces and are widely used in residential construction.
- Advantages: Efficient water drainage, longer lifespan, classic appearance
- Common Types: Gable roof, hip roof, gambrel roof
- Materials: Timber trusses, tiles, metal sheets
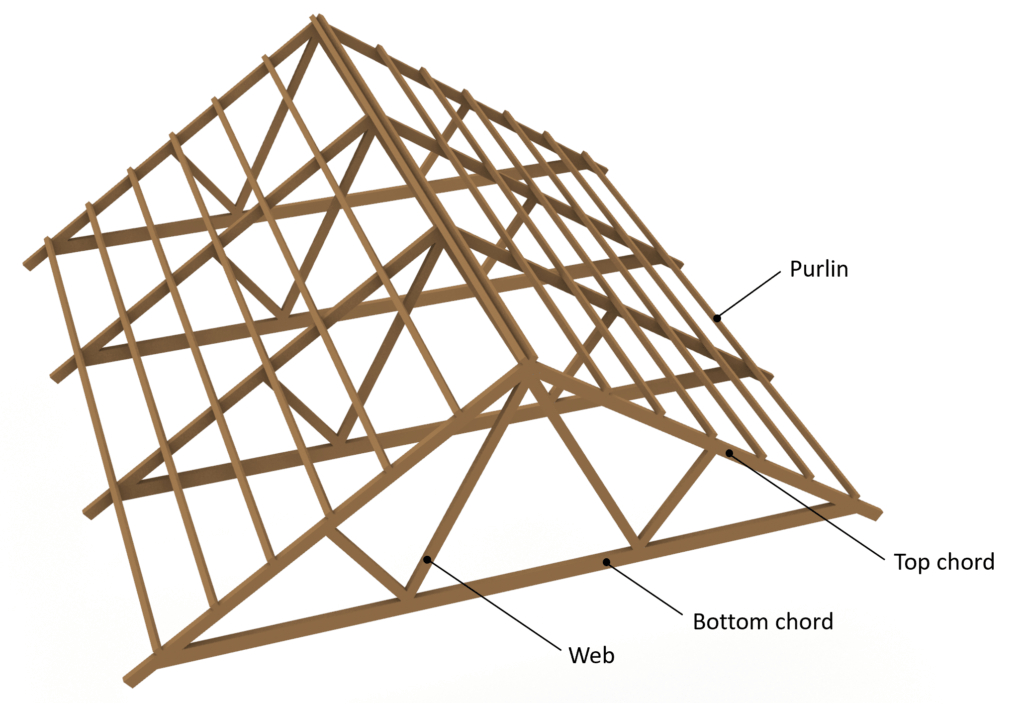
3. Truss Roof Structures
Trusses are prefabricated triangular frameworks designed to carry roof loads efficiently.
- Advantages: High strength, economical, suitable for large spans
- Materials: Timber, steel
4. Shell and Curved Roof Structures
These roofs are used in large-span buildings such as auditoriums and stadiums.
- Advantages: Architectural elegance, material efficiency
- Materials: Reinforced concrete, steel
Roofing Structural Components
- Rafters: Sloping members supporting the roof covering
- Trusses: Frameworks transferring roof loads to walls
- Purlins: Horizontal members supporting rafters or sheeting
- Battens: Fixing support for roof tiles or sheets
- Roof Covering: Final protective layer (tiles, sheets, shingles)
Materials Used in Roofing Structures
- Concrete
- Timber
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Clay tiles, slate, asphalt shingles
Importance of Proper Roofing Design
A properly designed roofing structure ensures safety, minimizes maintenance costs, improves energy efficiency, and extends the overall lifespan of the building. Structural design must consider load conditions, climate, and building usage.





